AN OVERVIEW OF GENE THERAPY
Ashok Chaudhary*, Rohit Barwar, Mayank Patel, Harsh Jogi and Prem Kumar ICAR- Indian Veterinary Research Institute, Izzatnagar, U.P.
* Corresponding author: drak97vet@gmail.com
1. Introduction
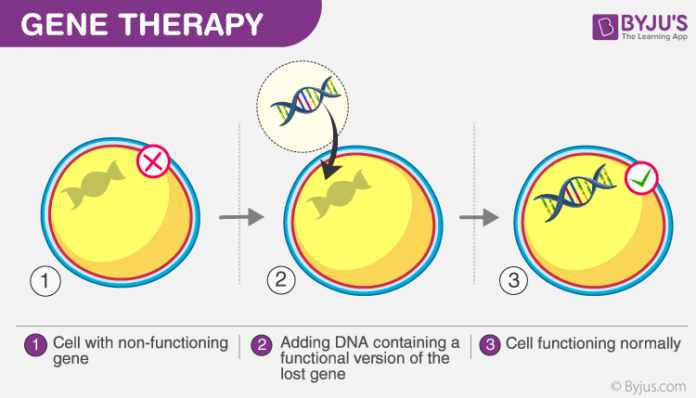
Gene therapy is a novel treatment method which utilizes genes or short oligonucleotide sequences as therapeutic molecules, instead of conventional drug compounds. This technique is widely used to treat those defective genes which contribute to disease development. Gene therapy involves the introduction of one or more foreign genes into an organism to treat hereditary or acquired genetic defects. In gene therapy, DNA encoding a therapeutic protein is packaged within a “vector”, which transports the DNA inside cells within the body. The disease is treated with minimal toxicity, by the expression of the inserted DNA by the cell machinery. In 1990 FDA for the first time approved a gene therapy experiment on ADA-SCID in the United States after the treatment of Ashanti DeSilva. In simple word Gene therapy is a technique which involves the replacement of defective genes with healthy ones in order to treat genetic disorders.
2. Types of gene therapy
There are several approaches for correcting faulty genes; the most common being the insertion of a normal gene into a specific location within the genome to replace a non functional gene. Gene therapy is classified into the following two types:
(a) Somatic gene therapy:
In somatic gene therapy, the somatic cells of a patient are targeted for foreign gene transfer. In this case the effects caused by the foreign gene is restricted to the individual patient only, and not inherited by the patient’s offspring or later generations.
(b) Germ line gene therapy:
In germ line gene therapy the functional genes, which are to be integrated into the genomes, are inserted in the germ cells, i.e., sperm or eggs. Targeting of germ cells makes the therapy heritable.
3. Gene Therapy Approaches
- Classical Gene Therapy
It involves therapeutic gene delivery and their optimum expression once inside the target cell. The foreign genes carry out following functions. Produce a product (protein) that the patient lacks; Produces toxin so that diseased cell is killed. Activate cells of the immune system so as to help in killing of diseased cells.
(b) Non-classical gene therapy
It involves the inhibition of expression of genes associated with the pathogenesis, or to correct a genetic defect and restore the normal gene expression.
4. Methods of gene therapy
There are mainly two method used for the transfer of genes in gene therapy:
(a) Transfer of genes into patient cells outside the body (ex vivo gene therapy)
In this mode of gene therapy genes are transferred to the cells grown in culture, transformed cells are selected, multiplied and then introduced into the patient.
(b) Transfer of genes directly to cells inside the body (in vivo)
In vivo method of gene transfer involves the transfer of cloned genes directly into the tissues of the patient. This is done in case of tissues whose individual cells cannot be cultured in vitro in sufficient numbers (like brain cells) and/or where re-implantation of the cultured cells in the patient is not efficient.
5. Vectors used for gene therapy
A gene cannot be directly inserted into a person’s cell. It must be transported to the cell using a carrier, or vector. Vector systems are two type:
- Viral Vectors
- Non-viral Vectors
Some Example of viral vectors like Adeno virus vector, Adeno-Associated virus vectors. Retro virus vectors and Herpes -simplex virus vectors. The example of non-viral vector is Injection of naked DNA. Physical methods to enhance delivery are Electroporation method, Gene gun method, Sonoporation, Magnetofection and Hydrodynamic delivery. Chemical. method to enhance delivery: Oligonucleotides, Lipoplexes and polymersomes.
6. Advantages of Gene Therapy
- Germline cell therapy cures the disease by altering the gene’s DNA sequence at the reproductive
- It has the ability to replace defective
- It can help in eradication of
- Gene therapy has the potential to eliminate and prevent hereditary diseases such as cystic fibrosis and is a possible cure for heart disease and
- Diabetes cured in dog by using gene
- Gene therapy can be used for cancer treatment to kill the cancerous
- Gene expression can be
- Therapeutic protein is continuously produced inside the body which also reduces the cost of treatment in long
7. Disadvantage of gene therapy
- Short lived nature of gene therapy which makes the patients to undergo multiple rounds of gene
- It is fact that wherever any foreign object in the form of pathogens, vectors or plasmids enter the body, the immune system of the body so response to it. It happens sometimes that immune response does not accept that foreign object and attacks
- Problems with viral vectors – Viruses, which is used as vehicles in most gene therapy, present a variety of potential problems to the patient-toxicity, immune and inflammatory responses, and gene control and targeting issues. In addition, there is always the fear that the viral vector, once inside the patient, may recover its ability to cause disease.
- In case of multi gene disorders, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, arthritis are caused by the combined effects of variations in many genes, such type of diseases would be especially difficult to treat effectively using gene
- It is not always probable that the vector will find the mutated cells, and if it does, it is not certain that the DNA sequence will be expressed. Therefore, better vectors must be developed that can successfully find the faulty cells and insert the DNA sequence
- Many diseases are polygenic, which means they are caused by several genes. In order for the treatment to be effective, the precise involvement of each gene and the proteins or enzymes for which they code must be determined.
8. Conclusion
Gene therapy is an emerging field of research and development that seeks new solution to pressing health and environmental problems by combining physical science and engineering with life sciences and medicine. Gene therapy represents the future of medicine and health but its growth is slow in the field application. The real challenge in transplantation is prevention of chronic rejection. The recent development of vectors capable of expressing a gene for extended periods of time has provided new tools to achieve this goal. Newer non-viral vehicles represent a valuable alternative, as they are nearly as efficient as, and potentially safer than viral vectors. Desirable features of future vectors include regulation of gene expression levels to match clinical needs tissue specific gene expression and multi-cistronic vectors controlled by oral intake of doxycycline or other agents have been tested successfully in vivo but still need to be optimized for clinical applications. Ensure that the genes that have been transplanted are precisely controlled by the body’s normal physiology signals.