FACTS & MYTHS REGARDING USE OF OXYTOCIN IN MILK LETDOWN & VETERINARY USE
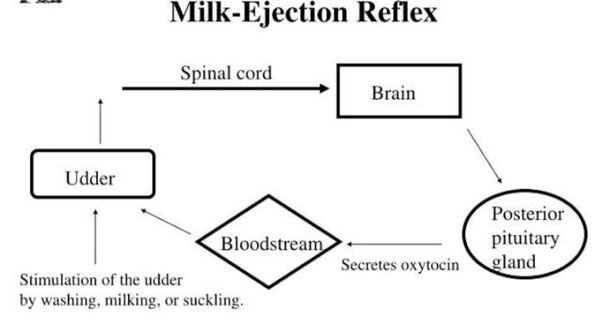
Hormone’ is a Greek word meaning “to set in motion”. Hormones are complex biochemical substances secreted in small amounts by various glands located in different parts of our body, each acting on specific organs. One such gland is the Pituitary, located in the base of the brain. Among several important hormones it secretes, one is oxytocin which is used to induce labour under the guidance of an expert doctor for conducting deliveries. Subsequently, the same hormone acts on the mother’s breast to eject milk so that she can feed her newborn.
Apart from these two well established actions one on the uterus and the other for release of breastmilk, the hormone is notorious for its abuse and misuse, which is probably because it’s popular by its other name as the ‘love hormone’. The spectrum of abuse ranges from being promoted to women to look younger and being used in agriculture by farmers to increase the size of vegetables and to increase milk secretion in cows. All these have no scientific basis, but the myths are so popular that oxytocin continues to be misused. So much so that the central Ministry of Health & Family Welfare issued a circular restricting “the manufacture of oxytocin formulations for domestic use to public sector only from September 1, 2018, due to complaints of misuse”. The implication of this circular is far-reaching because as of now over a hundred drug companies are manufacturing this drug. All of them would have to stop. Only one public sector company in Bengaluru would be permitted to manufacture oxytocin. The fear is that this will create a shortage of oxytocin, which is also a life-saving drug and finds mention in the World Health Organisation’s (WHO) list of ‘Essential Medicines’ as well as the union ministry’s own list. Restricted manufacturing will create a shortage of a life-saving drug because oxytocin is administered to prevent bleeding which may occur after the baby is delivered. Post-Partum Haemorrhage (PPH) or bleeding following delivery is a major cause of maternal deaths in India. Nigeria and India accounted for more than a third of all global maternal deaths in 2015, though these deaths have declined recently as per the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. But it is well-known that the single major medical cause of maternal death is PPH, because “more than 72.6% of deaths from haemorrhage were classified as postpartum haemorrhage”. So, the availability of affordable and good quality oxytocin is extremely important from a public health angle to prevent maternal deaths. Oxytocin is also used to induce unobstructed labour, which needs monitoring by health experts and this, in turn, reduces the chance of the mother needing to undergo Caesarean section.
Use in animals
Just as it is used in humans, so also oxytocin finds use in veterinary practice, to prevent bleeding after the calf is born. Often, oxytocin is administered to the cow about an hour or so before actually milking the cow. Many think that by injecting this drug, the milk yield will increase, but in reality it does not increase milk yield, it just hastens its flow. There is another misleading statement that is made: that when injected into the cow, its milk will contain oxytocin and is a health hazard to humans who consume it. This is an absolute myth because oxytocin does not act when taken by mouth and all standard textbooks all over the world have highlighted this aspect. For oxytocin to act, it has to be administered either by intramuscular or intravenous route. The drug does not act when administered orally, though at times it may be administered by inhalation through the nose either by intramuscular or intravenous route.
As a developing country, India depends mostly on agriculture and its livestock population. In India the livestock sector employs about 8 percent of the total population. India ranks one in terms of total livestock population as well as total milk production in the world. India contributes about 22 percent of the total global milk production. The increase in the demand for milk, has resulted in rampant use of various exogenous chemicals. One such incidence is the increase in the oxytocin supplementation. Oxytocin has been derived from the Greek word, which means quick birth. It is a peptide hormone synthesized in magnocellular-neuro-secretory-cells in supraoptic and paraventricular hypothalamic nuclei and stored in the posterior pituitary lobe then released in the blood as a result of a neuroendocrine reflex. It is transferred to the posterior pituitary after proteolytic processing and disulphide bond assembly Oxytocin is packaged in granules, then transported down with posterior-pituitary-gland axon and excreted to the systemic circulation with carrier protein, the neurophysin. Oxytocin, a neuropeptide, has 125 amino acid precursor. Apart from brain, Oxytocin is also synthesized in various other tissues and organs, including the uterine epithelium, ovary, testis, vascular endothelium and heart. It is now known that Oxytocin elicits its biological actions by binding to G-protein coupled receptor. In structural terms, oxytocin is a nano-peptide wherein the first cysteine residue is disulphide bonded to the 6th cysteine, thus creating partial cyclic peptide. The disulphide bridge in Oxytocin is essential for its interaction with the receptor and thus for biological activity.
Functions of Oxytocin
The oxytocin acts as the primary hormone for the ejection or let down of milk. Oxytocin is also involved in the process of parturition and in the management of post parturient uterine prolapse. It is used for the management of inevitable abortions and for the induction of abortions therapeutically. It is used for the treatment of cases like breast engorgement and mastitis, in the cases of agalactia and retention of fetal membrane. The release of oxytocin during suckling is to reinforce maternal behaviour. Oxytocin has insulinlike activity in that it stimulates lipogenesis and increases pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Oxytocin released during milking or suckling is to increase peripheral concentrations of lipids as part of a mechanism designed to replenish the lipids “lost” during milking or suckling. Moreover, prolactin and oxytocin are released during suckling and milking, and both prolactin and oxytocin have been implicated in regulation of fluid and osmotic balance.
Exogeneous Oxytocin Analogues
In order to duplicate the hormone and create an artificial drug Oxytocin (Syntocinon) was developed in 1953 by Vincent du Vigneaud. Other analogues used are Pitocin, carbetocin etc. The dose rate for Oxytocin in case of cattle for uterus inaction, milk ejection, mastitis, uterus involution is 40IU(I.M./S.C.) or 2.5-10 IU(I.V.). While in case of sheep and goat , exogenous oxytocin is used for milk ejection and uterus involution at the dose rate of 10-20 IU (I.M./S.C.) or 0.5-2.5 IU(I.V.), and in the case of uterus inaction, it is 10-20 IU (I.M./S.C.) or 0.5-2.5 IU(I.V.).
Milk Production and Oxytocin
Lactation consists of two phases: milk secretion or synthesis, which is controlled inpart by a hormonal complex originating in the anterior pituitary, and milk removal or (ejection), which is controlled primarily by oxytocin release from the posterior pituitary. The receptors for oxytocin are present in the smooth muscle cells and myoepithelial cells. The contraction of the myoepithelial cells result in the ejection of milk from mammary ducts. The receptors for oxytocin are also present in the myometrium and endometrium which gets activated at the end of pregnancy. The half-life of oxytocin is given by 2-8 minutes. Basal concentrations of oxytocin decreased from early to middle lactation, increased from middle to late lactation, and further increased from late lactation to the dry period.
Advantages of Oxytocin Injection
Effect on milk production:
There is an increase in milk production. There is increased gland milk output rather than residual milk removal. It is obvious that total evacuation of the udder during milking so that there is no-residual milk reduced production-losses which occur when using once a day milking, while ↑ the rate of milking was found ineffective in reduction of losses. Exogenous oxytocin injections at non-milking times ↑ the milk yield and improved galactopoiesis (maintainance of milk production). Thus, oxytocin influences cell maintenance and mammary metabolism in addition to its traditional role of facilitating milk let-down. The use of oxytocin to promote milk let-down, in particular when the glands are engorged with milk, can prevent udder damage and promote udder health.
Effect on milk composition:
Chronic oxytocin administration has also been shown to increase electrical conductivity and SCC of milk as well as lactose and K levels in the systemic circulation.
Effect on reproductive health:
Oxytocin is related to the reproductive process causing the womb to contract. Similarly, an oestrogen dominated myometrium such as is found at ovulation and at parturition, seems more responsive to oxytocin, and as a result, it causes greater contraction of the uterus. The release of oxytocin at that time is associated with subsequent myometrial contractions and appropriate stimuli that assist the transportation of sperm to the oviduct at copulation and helps in the expulsion of the foetus at parturition; hence plays an important role in the completion of the fertilization and parturition process. Oxytocin is also secreted into the blood in both females and males also at the sexual orgasm.
Disadvantages of Exogenous Oxytocin
Effect on milk production:
Milk let-down without administration of oxytocin seems to be difficult in the animals which regularly exposed to oxytocin injections as they become habitual to the drug. While repeated administration of oxytocin injections therefore interferes with the normal mammary epithelium milk secretary activity thus inhibits the normal milk ejection process and affect reproductive health. Thus a disadvantage of oxytocin injection was that its continuous usage could lead to addiction and lack of response to normal milk ejection stimuli.
Effect on reproduction:
It is believed that the prolonged use of oxytocin injections also causes fertility disorders like poor oestrus signs, reduced lactation period, lower conception rate and high embryonic mortalities. Delayed puberty, lower conception rates, increased abortion rates, lower pregnancy chances, delays in the duration of placenta expulsion, ovulation interval, shortened postpartum oestrus interval and calf death soon after the delivery because of poor quantity and quality of milk have also been observed.
Effect on human health:
Oxytocin produces its desired effects in minutes and then is readily metabolized in inactive products. It is mostly secreted and ingested along with the milk, it is efficiently degraded by gut enzymes so can’t reach the blood circulation in biologically active form. However ,it has been believed to have harmful effects when milk with oxytocin is consumed by humans. For example, oxytocin in milk and dairy products, the age at which girls attain menarche has come down drastically from 16 years of age to 10 years of age. Gynaecomastia (breast enlargement) is diagnosing even in boys due to oxytocin affects. Due toIt is clear to have imbalance hearing and weak eyesight in children due to oxytocin. Pregnant women should avoid such milk or don’t use milk without proper boiling. The use of such milk by the pregnant women may lead to abortion. And babies may born with deformities and low immunity levels. Use of such milk also increases the risk of haemorrhage in mothers after birth.
Since oxytocin is mostly known for let-down of milk , extensive use of oxytocin to increase the milk yield has let to harmful effects on the animals. There has been reduction in response to natural stimuli for let -down of milk. Moreover, the action of hormone causes the uterus of the cattle to contract, causing immense pain. Due to these reasons of extensive unethical use of oxytocin injection, Oxytocin is banned under Section 12 of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act (1960). According to Food and Consumable Substances Adulteration Act and the Drug Control Laws cannot be sold without a prescription from a registered medical practitioner. Thus, judicious use of exogeneous oxytocin supplements with proper consultancy can be helpful in terms of milk production as well as animal health.
Compiled & Shared by- Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.