Production of Designer Milk for Human Health: A Future Need
Milk can be designed to suit the needs of the consumers by suitably modifying its composition through nutritional interventions or transgenic methods. Designer milk is simply tailor made to provide the dual advantage of processing and health benefits to the consumers.
In an era where market is governed by customized commodities to meet the demands of the customers, designer milk satiates the palates of the consumers with more controlled and regulated supply of nutrients in the form of less fat and more protein. The need to search for customized milk called “designer milk” becomes more pertinent in the light of important role played by milk and dairy products. Milk and dairy products universally attract new born, kids, adolescents, adults and elderly alike.
To define, designer milk is nutritionally or genetically modified milk tailor made to consumer preferences, rich or poor, in specific milk components that offer the consumer greater health benefits. This novel initiative is possible because of the developments in genetic engineering and dairy biotechnology.
Milk contains many vital nutrients with biologically active peptides, immunoglobulins, immunoprotective agents and lactoferrin, etc. However, due to its high saturated fatty acid content, which is harmful to human health, milk and milk products have been criticised. On the other hand, dietary intake of unsaturated fatty acids reduces the risk of certain cancers, asthma and diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health conditions so by dietary manipulation we can alter the composition of according to human health benefits.
The dairy industry is at the brink of a transformative era, driven by scientific innovation and the growing demand for personalized health and nutrition. “Designer milk,” milk that is tailored to meet specific human health needs, is emerging as a promising solution to address various health concerns. With advancements in biotechnology and our understanding of the nutritional composition of milk, the production of designer milk is becoming a future necessity. This article explores the concept of designer milk, its potential applications in improving human health, and the challenges and opportunities associated with its production.
Relation between nutrition and health
In order to strengthen the immune system for the prevention of various diseases and thereby to improve health, dietary strategies may be effective alternatives. In Western and developing countries, consumption of milk and dairy products is increasing, but milk fat contains lauric, myristic and palmitic acids that increase the level of cholesterol, so it has a poor health impact, but some milk components such as conjugated linoleic acids, butyric acids and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (EPA & DHA) have health benefits and participates in chronic disease prevention. Whey proteins of milk also contain good amount antimicrobials, such as lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase, lysozyme, and immunoglobulins. Casein protein, vitamins A, E, K and D, probiotics, different minerals (calcium, phosphate, potassium, magnesium, chloride) and energy are also present in milk.
Designer Milk: What Is It?
Designer milk refers to milk that is intentionally modified, either through selective breeding or genetic engineering, to enhance its nutritional content and health benefits. It goes beyond the traditional concept of milk as a simple source of nutrition and aims to create dairy products that can address specific health concerns, provide additional nutrients, and even offer therapeutic properties. Designer milk can be customized to cater to the individualized nutritional needs of consumers.
Concept of Designer milk
Additional components with additional health benefits are found in designer milk. The composition of milk can be changed by dietary manipulation of milch animals to produce designer milk according to health needs. Designer milk has a higher proportion of unsaturated fatty acids (USFA) in milk fat, decreased lactose content so that people with lactose intolerance may use this milk and changes the protein and fat content of milk is improved the human health. Designer milk creates value-added dairy products with extended shelf life and improves milk yield and produces Nutraceuticals for milk-based products.
Applications of designer milk
The applicability of designer milk can be classified into two categories i.e. in diet and human health measures as well as in processing/technological developments. Among applications of designer milk in diet and human health is that it generates a greater proportion of Unsaturated Fatty Acids (USFA) in milk fat, reduced lactose content that benefits lactose intolerant individuals and removal of β-lacto-globulin from milk. However, it applicability in processing and technological developments includes alteration of primary structure of casein to improve technological properties of milk, production of high-protein milk, accelerated curd clotting time for cheese manufacturing, increased yield and/or more protein recovery, milk containing nutraceuticals and replacement for infant formula etc.
Relation between nutrition and health
In order to strengthen the immune system for the prevention of various diseases and thereby to improve health, dietary strategies may be effective alternatives. In western and developing countries, consumption of milk and dairy products is increasing, but milk fat contains lauric, myristic and palmitic acids that increase the level of cholesterol, so it has a poor health impact, but some milk components such as conjugated linoleic acids, butyric acids and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids have health benefits and participates in chronic disease prevention. Whey proteins of milk also contain good amount antimicrobials, such as lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase, lysozyme, and immunoglobulins. Casein protein, vitamins A, E, K and D, probiotics, different minerals (calcium, phosphate, potassium, magnesium, chloride) and energy are also present in milk.
Nutritional alterations to produce the designer milk
Less than 10% polyunsaturated fatty acids, less than 8% saturated fatty acids and more than 82% monounsaturated fatty acids are the ideal milk fat for human wellbeing. At different stages, the milk components may be altered. Rumen microbiota is the source of bioactive fatty acids in ruminants, which are incorporated into animal milk and meat. Dietary ingredients have an effect on milk composition of animals. Altering the composition of milk by dietary interventions is feasible .
The proportion of potentially safe milk fatty acids, oleic acid, vaccenic acid, rumenic acid, alpha-linolenic acid, and total polyunsaturated fatty acids increased in the diet of lactating cows by supplementing canola, soybean oil and linseed rich in alphalinolenic acid. In general, ruminant foods contain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFAs), but ruminant products such as meat or milk contain saturated fatty acids and certain quantities of Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLAs). This is due to the lipolysis of microbial enzymes and the bio-hydrogenation of rumen Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) . The main rumen-grown bio- hydrogenation bacteria are Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Manoeuvring the rumen environment creates opportunities to alter the lipid composition of meat and milk by modifying the disposition of intramuscular and mammary tissue Fatty Acids (FA) for absorption . Various probiotics or microbial feed supplements favourably alter lipid metabolism and modify milk composition. Phytometabolites such as tannins, polyphenol oxidase, essential oils, fatty acid oxygenation and saponins have various effects on the composition of the milk and increase the consistency of the milk. Pastured cow milk has a higher ratio of Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs) and grass-fed cow milk has higher conjugated linoleic acid than grain-fed animal milk. A varying number of microbiota or microbial metabolites of the rumen may also alter the composition of the milk. As the fatty acid composition of rumen microbiota is changed by the grazing regime, it can be used to change rumen microbial populations, thus changing the milk fatty acid profile . With the dietary addition of fish oils or fish meal, changes in milk fat concentration of Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) are also observed.
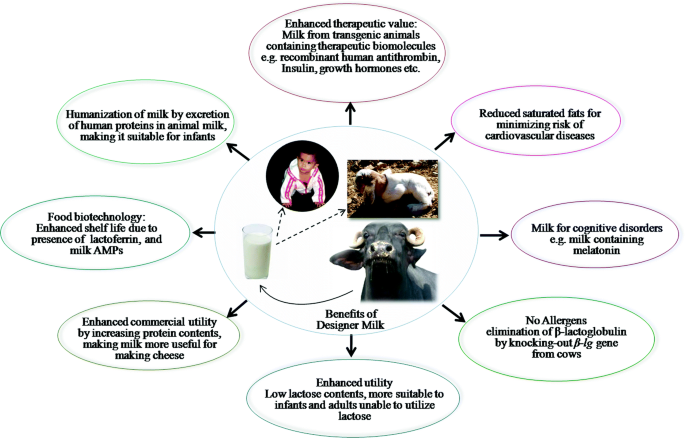
Benefits of designer milk
Eating designer milk has several health benefits that are:
- Reduce the problem of lactose intolerance by decreasing the lactose level in designer milk
- By increasing omega- fatty acids in the designer milk lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, allergies, obesity, and diabetes
- By minimizing saturated fats in the milk, lowering the incidences of obesity, cholesterol l levels, and cardiovascular diseases
- By altering protein contents, increasing casein to obtain an increase in cheese yield
- Phytosterol-enriched vitamin A milk decreases serum levels of triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and apolipoprotein-B that have a detrimental effect on health
Applications of Designer Milk for Human Health
- Enhanced Nutrient Profiles: Designer milk can be formulated to have higher levels of essential nutrients such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, offering potential solutions for nutritional deficiencies.
- Lactose-Free Variants: For individuals with lactose intolerance, designer milk can be engineered to have reduced or eliminated lactose content, allowing them to enjoy the benefits of dairy without digestive discomfort.
- Reduced Saturated Fat: Designer milk can be tailored to have lower levels of saturated fats, making it a heart-healthy option for those concerned about cardiovascular health.
- Probiotic-Enriched Milk: Incorporating beneficial probiotics into designer milk can promote digestive health, strengthen the immune system, and improve overall gut health.
- Milk for Special Diets: Designer milk can be formulated for specific dietary requirements, such as high-protein milk for athletes or low-calorie milk for weight management.
- Therapeutic Milk: Designer milk can even be developed to contain bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic benefits, such as antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory properties.
Challenges and Considerations
The production and adoption of designer milk come with several challenges and considerations:
- Safety and Regulation: Ensuring the safety of genetically modified organisms and their products is essential. Regulatory frameworks must be established and adhered to.
- Consumer Acceptance: Public perception of genetically modified or engineered foods can influence the acceptance and adoption of designer milk products. Educating consumers about their safety and benefits is crucial.
- Ethical Concerns: The ethical considerations surrounding genetic engineering and selective breeding need to be addressed. It’s essential to strike a balance between ethical practices and the potential benefits of designer milk.
- Sustainability: The environmental impact of designer milk production, including water usage and land resources, must be considered. Sustainable practices should be prioritized.
- Research and Development: Ongoing research is needed to further understand the health implications of designer milk and to optimize its nutritional profiles.
Opportunities and Future Outlook
The production of designer milk holds significant promise for the future. As advancements in biotechnology continue, there are several opportunities that lie ahead:
- Customized Nutrition: Designer milk can offer consumers a personalized approach to nutrition, meeting their specific health needs and preferences.
- Improved Public Health: Designer milk can contribute to reducing the prevalence of nutrient deficiencies and diet-related health conditions.
- Global Food Security: By enhancing the nutritional content of milk, designer milk can play a role in addressing food security challenges in regions with limited access to diverse food sources.
- Economic Viability: The development of designer milk products can create new economic opportunities for the dairy industry and support its long-term sustainability.
- Innovative Dairy Products: Designer milk can pave the way for a wide range of innovative dairy products that cater to evolving consumer demands.
Nutritional alterations to produce the Designer Milk
Less than 10 per cent polyunsaturated fatty acids, less than 8 per cent saturated fatty acids and more than 82 per cent monounsaturated fatty acids are the ideal milk fat for human wellbeing. At different stages, the milk components may be altered. Rumen microbiota is the source of bioactive fatty acids in ruminants, which are incorporated into animal milk and meat. Dietary ingredients have an effect on milk composition of animals. Altering the composition of milk by dietary interventions is feasible (Henno et al. 2018). The proportion of potentially safe milk fatty acids, oleic acid, vaccenic acid, rumenic acid, alpha-linolenic acid, and total polyunsaturated fatty acids increased in the diet of lactating cows by supplementing canola, soybean oil and linseed rich in alpha-linolenic acid. In general, ruminant foods contain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), but ruminant products such as meat or milk contain saturated fatty acids and certain quantities of conjugated linoleic acid (CLAs). This is due to the lipolysis of microbial enzymes and the bio-hydrogenation of rumen polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) (Lourenço et al. 2010). The main rumen-grown biohydrogenation bacteria are Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens. Manoeuvring the rumen environment creates opportunities to alter the lipid composition of meat and milk by modifying the disposition of intramuscular and mammary tissue fatty acids (FA) for absorption (Toral et al. 2018). Various probiotics or microbial feed supplements favourably alter lipid metabolism and modify milk composition. Phytometabolites such as tannins, polyphenol oxidase, essential oils, fatty acid oxygenation and saponins have various effects on the composition of the milk and increase the consistency of the milk. Pastured cow milk has a higher ratio of essential fatty acids (EFAs) and grass-fed cow milk has higher conjugated linoleic acid than grain-fed animal milk. A varying number of microbiota or microbial metabolites of the rumen may also alter the composition of the milk. As the fatty acid composition of rumen microbiota is changed by the grazing regime, it can be used to change rumen microbial populations, thus changing the milk fatty acid profile (Bainbridge et al. 2018). With the dietary addition of fish oils or fish meal, changes in milk fat concentration of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) are also observed.
What is new in designer milk from the dietary and health point of view?
- To increase the proportion of unsaturated fatty acids in milk and thereby lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases, especially, for the obese middle aged and elderly people.
- To reduce lactose content of milk, thus paving the way for better acceptance by lactose intolerant persons.
- To remove the beta lactoglobulin from milk which is sometimes associated with allergy in children.
The novelty from the technological angle
- Altering the primary structure of casein to improve technological properties of milk
- Engineering milk in such a way that results in accelerated curd ripening and better yield during the cheese making process.
- Milk with the much needed high protein content
- Nutraceutical milk containing human therapeutic proteins
- A suitable replacement for infant milk formula.
What is modified in the milk to make it designer?
There are two methods viz. nutritional interventions and transgenic animals by which the fat, protein and lactose content of the milk can be altered.
Nutritional interventions
The result can be achieved by suitably altering the feeding pattern of the dairy cows.
Milk fat : In general, milk contains 3 to 4% milk fat. The majority of the fatty acids in milk are saturated with 4 to 18 carbon atoms (short chain). The rest are mono unsaturated (16:1 and 18:1) and ploy unsaturated (18:2 and 18:3). From the saturation point of view, milk contains 70% saturated fatty acids, 25% mono-unsaturated and 5% poly-unsaturated fatty acids.
Majority of the dairy scientists are of the opinion that the ideal milk shall contain less than 10% poly-unsaturated fatty acids, less than 8% saturated fatty acids and more than 82% mono-unsaturated fatty acids. The modification of milk fat can be achieved by decreasing the level of saturated fatty acids, increasing the level of conjugated linoleic acid content and increasing the omega 3 fatty acids in milk.
Saturated fatty acids: They are often accused as culprits associated with heart diseases because of their ability to the blood cholesterol. But not all the saturated fatty acids are bad. The fatty acids with less than 12 carbon atoms, in fact, decrease the cholesterol content since they are all catabolised. The real culprits are Lauric (C12:0), Myristic (C14:0) and Palmitic (C16:0) which increase the plasma concentration of cholesterol. Their share is 44% in the total milk fatty acids.
Feeding of dairy cows with unsaturated fats in protected form through encapsulation increases the unsaturated fat content in milk. However, the unsaturated fatty acids are converted into saturated one in the rumen by the rumen microorganisms. To prevent this, rumen by pass is the only way out. This can be achieved when small droplets of lipids are encapsulated in thin layer of protein through formaldehyde treatment and fed to the dairy cows. Doubling the spreadability of butter is achieved when a special blend of canola and soy bean meal in protected form is fed to dairy cows because the melting point of milk fat containing unsaturated fatty acid is higher.
How to increase the Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) content in milk?
CLA is a product synthesized in rumen due to bio-hydrogenation of linoleic acid. The bio-hydrogenation adds hydrogen atoms to unsaturated fatty acids. The cis-9, trans-11 is the most common isomer in ruminant products and accounts for more than 90% of the CLA in milk. A diet rich in linoleic and linolenic acids in the form of oil / seeds increases the CLA levels in milk fat two fold when oil is accessible to the rumen microorganisms for bio-hydrogenation. Milk from grass fed animals is known to contain five times higher CLA level than those fed with grain.
Conclusion
Consuming designer milk and milk products improves human health and well-being. Animal nutritional intervention, with an increasing interest in functional and nutraceutical foods, can easily help design milk with various functions and utility. Some important compounds like carotene, needed for normal body function cannot be synthesized by the human body can easily be fortified and supplemented by designer milk.
The production of designer milk for human health is not merely a concept of the future; it is a necessity driven by the demand for personalized nutrition and improved health outcomes. With the potential to address nutrient deficiencies, dietary concerns, and even therapeutic needs, designer milk represents an exciting frontier in the dairy industry. To realize its full potential, it is essential to address regulatory, ethical, and sustainability concerns, while continuing to advance the science and technology that underpins this groundbreaking development. Designer milk has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach dairy nutrition, making it not just a source of sustenance, but a source of tailored, targeted, and transformative health benefits.
Compiled & Shared by- This paper is a compilation of groupwork provided by the
Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.