APPLICATION OF OZONE THERAPY IN VETERINARY FIELD
Compiled & Edited by- Dr.Mishraa Aashutosh,TVO (Touring Veterinary Officer) , Jahanabad , Animal And Fisheries Resources Department, Government of Bihar
Innovative, effective and safe, ozone therapy is being used in veterinary medicine for everything from ear infections to cancer.
Ozone therapy might sound like something new, but it has been around for over a century, at least when it comes to human healthcare. More recently, however, it was also introduced to the veterinary world, where it’s being successfully used to help treat a range of conditions in dogs and cats.
Ozone was first discovered in the late 1800′s. The first uses included the purification of water, and today, cities the world over use ozone to purify drinking water. Ozone is unique in that all microbes are susceptible to its oxidizing powers without the development of resistance. Ozone was successfully used to treat infected wounds during the first world war, and today medical ozone therapy is common throughout Europe.
Ozone, (O3), is an energized form of oxygen which contains three atoms of oxygen, rather than the two oxygen atoms that we normally breathe. Ozone is a powerful sterilizer that destroys bacteria, viruses, and odors. The extra oxygen atom in ozone makes it reactive, allowing the atom to attach itself to other molecules. When contaminants such as bacteria or viruses make contact with ozone, it breaks down cell walls, thus destroying bacteria in a process is called oxidation. Ozone essentially reverts back to oxygen after it is used, making it a relatively safe and environmentally friendly treatment option. Ozone is naturally found, most often as a result of lightning strikes (think of that “clean smell” before or after storms), and within the “ozone layer” that encircles the Earth outside the atmosphere.
Ozone is relatively safe if used correctly. High concentrations of ozone in the air can cause health problems. Extended exposure to very elevated levels of ozone can cause irritation to the lungs.
Ozone and other oxygen therapies have been used for over 100 years around the world for human and animal healing. These therapies continue to gain popularity, as scientists learn about the health benefits of increased oxygen in the body. Currently, ozone therapy and hyperbaric treatments, which bring easily soluble oxygen to target tissues, are being proven effective for treating viruses, fungi and bacteria, and for general health improvement anytime there is inflammation and damaged tissue. In addition to medical uses, ozone is a great disinfectant used for livestock water tanks, cattle embryo transfer(tt), swimming pools, spas and the water treatment systems of over 2,000 municipalities around the world.
How it works
Ozone contains three oxygen atoms, which react in the tissue as it breaks down to ordinary oxygen (O2) and a reactive singlet oxygen molecule that can combine with chemicals and other molecules. Free from side effects, this is an extremely safe therapy that works in a number of ways by:
- Decreasing inflammation. When you have inflammation, swelling, bruising, infection, cancer and trauma to the tissue, there are higher amounts of carbon dioxide within the tissue. This increase of carbon dioxide contributes to inflammation and pain. Increasing the amount of oxygen delivered to the tissue in the form of reactive ozone decreases inflammation, pain and swelling, and helps increase healing.
- Activating the immune system. Ozone therapy has also been shown to activate the immune system by stimulating cytokine production. Cytokines are “messenger cells”, such as interferons and interleukins, which “set off a cascade reaction of positive changes throughout the immune system.”(t). Ozone also promotes the production of glutathione peroxidase, catalase, reductase and super-oxide dismutase, the enzymes forming the cell wall coating; thereby enhancing cellular immunity. 3.Inactivating bacteria, viruses, fungi, yeast and protozoa. Healthy cells are surrounded by an enzyme coating, which ozone does not penetrate, but bacteria and viruses have no such coatings. Ozone therapy disrupts the integrity of the bacterial cell envelope through oxidation of the phospholipids and lipoproteins (peroxidation). In viruses, this peroxidation disrupts the reproductive cycle and damages the viral capsid. In fungi, ozone inhibits cell growth. Consider chronic otitis, which often has multiple organisms as primary or secondary invaders; this explains the efficacy of ozone treatment.
Medical Properties of Ozone

Ozone has several properties which make it perfect for medical use:
- Ozone is a potent regulator of the immune system
- Ozone stimulates increased uptake and utilization of oxygen
- Ozone increases the efficiency of the body’s antioxidant enzyme system
- Ozone improves circulation
- Ozone is anti-inflammatory
- Ozone is anti-microbial
Medical conditions that may benefit from ozone therapy:
- Cancer
- Auto-immune disease
- Chronic infections such as hepatitis, cystitis, Lymes disease, etc.
- Allergies, sinusitis
- Intestinal diseases
- Ear infections
- Dental infections
- Arthritis, degenerative joint disease, chronic pain
- Degenerative backs
How is ozone medically administered?
- Major or minor autohemotherapy (mixing ozone with blood and re-infusing)
- Dissolved in IV fluid solutions ( saline or distilled water)
- Intestinal insufflations (rectal & vaginal)
- Auricular insufflations
- Limb bagging
- Topical exposure (ozonated olive oil)
- Joint or subcutaneous injections (Prolozone)
Administration options
Since ozone helps with the healing of any problem, it can be added to any treatment protocol.
- Percolate into saline fluids to be used as a flush (decreases inflammation and pain) to wounds, bladder, rectum, ear, nose, mouth; enema; IV or SQ fluids to be absorbed through the capillaries of the subcutaneous tissue.
- Percolate through olive oil with or without essential oils for the skin.
- As a gas via a catheter, internally, or by sealing a wounded area in a bag (old fluid bags work well). It will be absorbed through the caudal rectal vein.
- Injected as a gas into joints with a prolotherapy injection (prolozone). Human study1 showed efficacy in pain relief for many conditions.
An added technique using ozone is Biophotonic Blood Therapy (BBT), in which blood is infused with ozone, exposed to ultraviolet light in a crystal cuvette, and then given back to the patient. Also called Ultraviolet Blood Irradiation, it has been used worldwide for over 50 years for an array of medical conditions. It may be more effective than mere ozone for stimulating cytokines and activating the mitochondria in each cell to strengthen an animal’s immune system.
Ozone preparation
Oxygen as a single molecule is highly unstable and exists for only microseconds in nature. However, when two oxygen atoms unite to share electrons, they form an oxygen molecule, referred to as O2. This molecule is very stable, and comprises the form of oxygen found in the atmosphere. To create ozone, pure surgical oxygen (ordinary air cannot be used as it has 20% nitrogen which would be converted to nitrous oxide and nitric oxide, both highly toxic) is flowed through a glass tube (do not use models with plastic tubing). A low voltage electrical spark is then applied through the outside of the tube. This briefly splits the paired oxygen atoms, most of which reform into pairs within microseconds. A small percentage of the individual oxygen atoms form triplets – ozone (O3). The ozone produced exists in a very active form for about 30 minutes before breaking down (dismutating) into two atoms of oxygen, which are very easily absorbed into the cells, by giving up one atom of singlet oxygen. Ozone will dismutate at a rate of 50% every 45 minutes in glass, and every 30 minutes in plastic. Therefore the ozone cannot be stored and used later.
Uses are many and varied
Any time there are infections or inflammation, tissue damage or abnormal cellular proliferation, ozone can be use to support treatments, conventional or holistic. A few examples are:
- Skin – wounds, especially degloving ones and deep abrasions; hot spots; pyodermas; allergic dermatitis; abscesses
- Pain relief
- Head trauma, spinal cord inflammation–ozone and oxygen go through the blood/brain barrier so it is an excellent way to aid treatment of any neurological issue
- Chronic and acute Lyme disease
- Mouth–stomatitis, gingivitis, abscesses; ozone therapy is ADA-approved for dental abscesses
- Cancer and autoimmune problems
- Ears – chronic and acute otitis from bacteria or yeast; aural hematomas
- Eyes – infections and allergic reactions
- Upper respiratory ailments
- Potentiates acupuncture, homeopathy and chiropractic treatments as it brings more needed oxygen to the body
- GI tract – constipation, diarrhea, IBS (decreases inflammation)
- Equine infectious anemia
Integrating ozone into your veterinary clinic protocols gives you a wonderful opportunity to use something very natural and sustainable that can reduce and possibly prevent the overuse of antibiotics and drugs. Technicians can administer ozone in most of its applications. As a holistic integrative veterinarian, I think it potentiates some of the other natural modalities I use, such as acupuncture, homeopathy, herbs and chiropractic. Antibiotics are also more effective with ozone as an adjunct. It is also a practice builder, since clients are searching for supportive ways to help their pets. With training, pet owners can get an ozone unit and administer it in a variety of ways themselves. Because ozone is antiviral, it should be a must for any animal shelter that deals with a lot of infectious viruses.
Reference-Margo Roman, DVM, CVA, COT, CPT
Ozone therapy is safe and acts in several ways:
- It decreases inflammation.
- It activates the immune system by stimulating cytokine production. Cytokines such as interleukin and interferons create positive immune stimulation.
- Ozone inactivates bacteria, fungi, viruses and yeast. Healthy cells are surrounded by an enzyme coating, which ozone does not penetrate. But bacteria and viruses have no such coating, thus the O1molecule penetrates and kills the invaders. Consider chronic otitis (ear infections), which often have multiple bacteria, yeast and sometimes fungus — the efficacy of ozone therapy in these cases is amazing.
How is ozone administered?
There are multiple ways to use ozone in both humans and animals, making it easy to add to traditional therapies, or for use in acute or chronic cases. Here are just some examples:
- Intravenous fluids can be ozonated and run into the body intravenously. This method can be used for Lyme disease, septicemia, liver, kidney infections and more.
- Ozone may be percolated through olive oil and used in an incubator as an inhalant. This is great for upper and lower respiratory infections. (Ozone gas cannotbe used directly for inhalation as it is extremely drying and irritating.)
- Ozone may be injected into the joints for infections or used in prolotherapy for tendons and ligaments.
- Ozonated olive oil (or other oils) can be used topically for wounds – and even for the eyes.
- Ozone may be used as a urinary insufflation for chronic urinary infections.
- It may be infused rectally for a variety of gastrointestinal issues, and for GI tumors!
- It can be injected directly into a tumor.
- Injecting ozone directly into the bloodstream as a gas is controversial, but I personally know physicians and veterinarians who do it. Ozone dissolves so quickly into O1 and O2 that no gas emboli are formed

METHODS OF ADMINISTRATION (Figure 1)
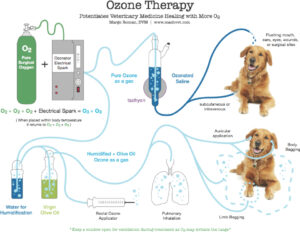
Saline 0.9% Percolated with Ozone
- Subcutaneous fluid given to patients which gets into the blood stream and through the blood–brain barrier
- Flushing external wounds
- Hot spots, bite wounds, infected and slow healing wounds, postsurgical areas
- Flushing gums and mouth before, during and after dentals with or without extractions.
- Flushing eyes and other orifices
- Eye injuries and infections
- Vaginal and preputial infections
- Flushing and cleaning ears.
- Flushing infected surgical sites including abdominal contamination
- Lavaging the abdomen with ozonated saline when contamination
- Flushing intestinal incisions, enterotomies and intestinal anastomosis
- Flushing urinary catheterized animal to bath the bladder and cleanse surface and help flush out calculi
- While taking a culture of the urine in the bladder, after removing sample, inject ozonated saline directly into the bladder.
- Giving the ozonated fluids over an area that is sore or bruised; then do your acupuncture/aquapuncture through that fluid, and help driving the ozone as it is pushed through with the needle
- Giving the ozonated saline as an IV treatment and running some ozone gas directly into the line for a higher percentage
- Stomach lavage after ingestion of toxic material
- Lavaging through a stomach tube, chocolate or other substances that can be removed through stomach pumping
- As an enema for both cats and dogs. It will bring down the irritation of the colon from the constipation and some of the pain of the procedure.
-
- lavaging multiple times can cool the animal and can be used for hyperthermia
- Bagging limbs and flushing areas that have infections or inflammation
- Interdigital infection, toe infections, wounds, pyoderma, Malassezia, tumor
Insufflated rectally
, it will be bubbled through water to add moisture. Keep the tail tucked and sealed over the anus to prevent the gas from escaping for about 10 minutes
-
- For whole body administration
- To get into an inflamed colon
- Direct uptake into the caudal mesenteric vessels into the liver
- for hepatitis and pancreatitis
- Delivered when there is a concern for cooling temperature of the saline.
- Delivered when there is a blood pressure or concern about too much fluid retention due to the saline
- With cardiac cases
- Hypothermic patients
- Animals on blood pressure medications
- To give a higher amount of ozone without the carrying fluid
Ozonated air bubbled through water and virgin olive oil
-
- Auricular bagging or through a stethoscope
- All the above limb bagging for a lessened ozone odor and lung irritation
- Whole body bagging
- Whole animal placed in a close cage
- Any time you have others in the room as to lessen the smell and possible reaction
Ozonated Water
-
- Drinking directly after making
- Washing off your tables due to virus and bacteria
- Giving as a water source after dentals
Intravenous Treatments
-
- In Horses, IV catheter placed in jugular vein small with 25-gauge needle, bubbled as a pure O3 gas toward heart slowly
- Also given with ozonated saline charged
Ozone as a gas as a 5 setting 61 gamma
-
- Injected into a tumor
- Injected into an infected area
Ozonated olive oil or other oils: Jojoba, olive
-
- Can purchase products that have been ozonated for a week
- Can generate ozonated olive oil by ozonating organic virgin olive oil for about 50+ hours and keep it in refrigeration.
- Better to make it up in small glass dropper bottles.
- Can add before or after essential oils of lavender, frankincense, neem
- These can be applied topically and to gums
- Can be applied as a rectal suppository for rectal inflammation and tumors
Prolozone:
Prolotherapy with ozone as a flush behind the B12, Procaine, Dextrose and Homeopthic Combination. You can also add Sodium Morrhuate. Use equal volumes of liquid to ozone. The Prolo cocktail I use is from Dr. Roger DeHann’s combination. There are pre-made prolotherapy solutions from several compounding pharmacies. His typical solution is a combination of 25% of the four following ingredients
-
- 50 % dextrose
- 2 % lidocaine or procaine (without epinephrine)
- B12 at 1000 mcg/ml
- Biosode or a homeopathic Heel remedy like Traumeel or Zeel liquid
- The 50% Dextrose is the Key Ingredient in proliferation therapy (can use Sodium Morulate); it can stimulate fibroblast activity. The other ingredients are supportive and synergistic
- Lidocaine or Procaine has a dual purpose: first there is a mild anesthetic effect; second, it also helps increase cell membrane electricity and activate the healing process when there is electrical stagnation. Neural therapy is part of this.
- B12, which helps to decrease the pain and has a tonic affect and helps increase healing by positively balancing membrane electricity.
- Biosode, Traumeel or other related homeopathics have their own benefits. Injected they may be 20–100x more effective than taken orally. This helps synergizes the rate of healing in a positive way
Sometimes you can mix delivery of both saline and then rectal air to accommodate to the need of the patient. Ozone can be used for arthritis, disk herniation, hip degeneration, cruciate injury, and ligament injury. It can help stimulate healing.
DOSAGES
Using the Venmar and Longevity charts give a range. Using a 1/8 flow of Oxygen and setting of 7 on the longevity 84 gamma and 8 on the Venmar 51gamma (see the charts below).
PRECAUTIONS
-
- DO NOT breathe ozone directly, because it will cause irritation in lungs. If taken within lungs it must go through olive oil. You can run the gas through water and olive oil, too.
- Having the pets on vitamin C or other antioxidants is important to protect against free radicals. Give animals vitamin C subcutaneously (SC) as an injection around 10 minutes after the SC and rectal ozone.
- Some bleeding can occur with thrombocytopenic patients at the site of the subcutaneous administration.
- Warn clients that the subcutaneous administration is cold and pets may squirm as if someone has but a cold towel on their back. Good distraction with cookies or upbeat conversations will help. Some of the animals may object with crying.
- Fluids may be too cooling for the hypothermic patient. Warming may lose some the ozone percentage. Giving more rectal ozone instead of SC will reduce the cooling affects of O3 therapy.
- When dispensing subcutaneous ozonated fluids for a pet, be sure to know the temperature of the pet, as the fluids are cold and will take the body temperature down. Keep the temperature at least 100 degrees before giving fluids.
- Some dogs seem itchy at the site so allowing them to “shake it off” after treatment is good.
- Keep windows open or have a vented area when bagging, as it might cause some to have irritation of the throat.
- Always check the connections of the silicon tubing.
- Use only silicone tubing, because it will break down regular rubber and some soft plastic or Latex.
- Be careful to keep any equipment that has black rubber away from the ozone; that includes anesthesia breathing bags as it will break down the rubber.
- Ozone will dissolve Latex gloves when present as a gas.
- Do not leave the ozonator on without the oxygen connected.
- Always use 100% oxygen running through the ozone generator; do not use room air.
- Some people are sensitive to the ozone, so make sure your techs or clients are not having any sensitivities.
- When placing a rectal catheter make sure after removing you pull the tail between rear legs to prevent “passing of the gas” before it has a chance to be absorbed.
- You are using O2 so all precaution to an O2-rich environment should be observed.
SUGGESTIONS AND APPLICATIONS
-
- Before bagging the ears or wounds, first flush well with the ozonated saline to clean off the surface; making the surfaces moist also helps the process.
- Use the largest needle to get the fastest fluid administration and therefore have less O3 converting to O2 in the plastic tubing.
- Roll the IV bags to deliver the ozone even faster.
- Keeping the IV line attached with a needle will allow a more directed flush onto the eyes and any direct area.
- When loading a syringe, the ozone is heavier than air so you need to keep the needle opening upward. Placing a needle with cap on it gives you more flexibility to where it is placed prior to administering.
- When starting a cylinder with 1000 cc of ozone allow it to perk for 30 minutes at 1/8 oxygen and 10 setting.
- Ozone will stay stable for about 30 minutes, so use it as soon as you can to get the maximum amount stored in the saline.
- It stays longer in glass than the plastic.
- Giving the ozonated fluids cooled gives you more time to assure that the O3 is still present.
- If you need to warm the ozone, take a thin water bottle filled with warm water and at the end of the IV drip wrap the plastic tubing around the bottle.
- When giving rectal gas to an animal, you can give more ozone and have less issue with fluids being too cold and reducing body temperature
- You want to use up the ozone as close to the time of production, so plan out your strategy, as time loses the percentage of O3.
- When bagging or whole body, try to seal the opening to keep leakage to a minimum.
- Attachment of energetic discs like tachyon around the cylinder might even energize the water even more.
- The IV pole can be top heavy, and it is important to counter balance the pole, or you could have the pole fall over and crash to floor. The IV apparatus is hard to get and costly.
- Re-perk your ozone after 20 minutes of not being used.
- Having a second fluid delivery apparatus gives you a constant readiness of fresh ozone to be used.
- Line up several animals to be given ozone in each of the rooms and then take your fluid delivery apparatus (FDA) to each room.
- Can dispense into plastic IV bag; kept on ice, it can last about 2 hours. Give as soon as you can.
- Can dispense in glass and refrigerated and we have have seen it seem to have ozone last 2 days.
- When it loses its O3 it is just sterile saline so is useful. Great for any external flushing
CONDITIONS TREATED
-
- All types of wounds, skin infections hot spots, pyodermas, abscesses, rashes, allergic dermatitis, insect bites, gangrenous lesions, deep abrasions with road dirt contamination, severe contusions de-gloving wounds, postsurgical flushing directly on incision and area treated.
- Chronic and acute Lyme disease.
- Giving ozone before giving any acupuncture or homeopathy to make the tissue more hydrated and oxygenated.
- Acute and chronic kidney and liver failure
- Pancreatitis
- Viral and bacterial diarrhea
- Spinal and head injuries
- Musculoskeletal injuries
- Cancer adjunct therapy
- Stomatitis and gingivitis
- Ocular irritations, allergic and infectious
- Yeast-filled ears and both acute and chronic otitis
- Upper respiratory conditions both viral and bacterial
- Autoimmune conditions
- Irritable bowel and leaky gut syndrome
- Use instead of antibiotics if there has been a reaction or toxic reaction.
- Potentiates acupuncture, homeopathy, and chiropractic and other modalities as it brings more needed oxygen to the body.
- Seizures
- Pain from injury or musculoskeletal issues as it brings the circulation to the area.
- Lavaging stomach due to toxin ingestion, such as chocolate.
- As saline enemas for obstipation reduces the pain.
- Ear hematoma.
- Corneal and eye infections and trauma, ulcers as well.
- Flushing cystotomies and enterotomy sites.
- Flushing the entire abdomen post exploratory.
INJECTING WITH OZONATED GAS
-
- Injecting gas into a tumor
- Setting at 5 on Longevity or 61 gamma
- Volume of air injected: about half to 3/4 size of mass. Will blow up like a balloon. Will dissipate.
- Use a very small/long needle (25-gauge and 1½-inch).
- Injecting gas into an infection and into infected gums and roots.
- Injecting gas into a tumor
DENTAL OZONE
-
- Apply ozonated saline as a mouthwash before the dental. Using it as a flush through the dental procedure. Flushing pockets and gum line reduces inflammation and removes high bacteria load and reduces Biofilm.
- Give subcutaneous ozonated saline during the dental to brings down the inflammation, reduce the pain, and decrease need for antibiotics.
Some applications that I would like to see more cases of ozone therapy in include removing blood from an auricular hematoma with a needle and placing about 3 cc of ozonated air as a bubble pressure bandage; place a soft splint type bandage to allow the ear to heal and shrink, and keep bandage on for 10 days.
DOSAGES AND SETTING
Dosages can vary and I have not been able to exactly determine how much ozonated saline to give. My criteria is that if an animal does not have an underlying heart problem or suspected increased blood pressure problem, I will give about 60% ozonated saline (for the day) than if it was just plain saline. If there is an underlying issue, I will give about 30%. I will increase the rectal gas amount as that does not increase the NaCl. If an animal has a low body temperature, I will give it warmed Lactated Ringers fluids and wait for the temperature to rise before giving the ozonated fluids, and then will give small amounts. These really critical animals cannot afford to become even more hypothermic. If one warms the ozone, you will probably lose the gas suspended in the fluids. I will sometimes place a warm bottle at the last part of the IV line.
IV FLUIDS
Settings: Saline, 1/8 liter/minute and 7 or 8 setting
OZONE
Start with lower amounts until the animal gets used to the cold sensation and gets used to the ozone level, which can cause the animal to get a little light headed
Follow the recommended chart with your particular ozonator.
Ozone has the positive support for tissue repair and could be part of veterinary procedures.
If the animal cannot take the coolness of fluids, you can use part of the rectal amount and part of the subcutaneous fluid.
If an animal is hypothermic, give warmed Lactated fluids and warmed towels/bottles to bring temperature to at least 100°F, and then give rectal ozone.
EQUINE USE
For horses, it can be given rectally or intravenously For rectal administration, fill a 1000-cc plastic IV bag with ozone and connect to a rectal catheter. Roll the bag like a tube of toothpaste. You then can remove the catheter and pinch off the anus holding it tight until your fingers cannot hold it. Repeat after 20 minutes if you want.
You can also get a large syringe, 150 cc, and infuse gas at 51 gamma. My 1000-lb horse worked up to 500 cc after 3 months.
Use a 25-gauge 1½-needle and tap into the jugular vein and bubble slowly into the vein. You can hear it bubbling into the vein. Go slowly initially, then you can give it a little faster. You don’t need to use a formal catheter but just the needle, which you can easily tape to the neck and have an extension so you can stand slightly away from the animal. You can use the same site each time. Ozone therapy can be given daily, or several times a week, or once a week.
RESOURCES
-
- Altman N. The Oxygen Prescription The Miracle of Oxidative Therapies, Healing Arts Press, 2007.
- Boccii V. OZONE, A New Medical Drug, Springer science+Business Media, 2011.
- McCabe E. Flood Your Body with Oxygen Therapy for a Polluted World, Energy Publications, 2nd ed., 2010.
- Shallenberger F. Principles and application of Ozone Therapy: A Practical Guide for Physicians, 2011.
- Longevity Resources


