From Grazing to Zero-Grazing (Stall fed ) Goat Farming in India
Goats are among the main meat-producing animals in India , whose meat (chevon) is one of the choicest meats and has huge domestic demand. Due to its good economic prospects, goat rearing under intensive and semi-intensive system for commercial production has been gaining momentum for the past couple of years. High demand for goat and its products with potential of good economic returns have been deriving many progressive farmers, businessmen, professionals, ex-servicemen and educated youths to take up the goat enterprise on a commercial scale. The emerging favourable market conditions and easy accessibility to improved goat technologies are also catching the attention of entrepreneurs.
India is a country with diversity. We find all types of cultures, clothing and food habits. Globalization has added a lot to our food menu also. Non-vegetarian dishes are common along with vegetarian items. Beef and pork are not that popular in India compared to western countries. Hence goat-sheep-chicken and fish are the main source of non-veg. food. Availability of wild animals has comedown drastically. Traditional animal husbandry is losing its base against commercial mono-culture system of modern agriculture. Even the villagers are depending on chicken-mutton stalls of cities. This has created tremendous scope for commercial poultry, goat and sheep farms. This article explains each and every detail of goat farming in India.
Goat is the first domesticated animal even earlier to cow. We still find related animal species in the forest. Goat is the hardy creature compared to sheep and cattle. It prefers the driest climate. Even then it can survive in heavy rainfall area under protected rearing system. We do not find sheep in forest region and coastal belt. But goat farms are seen everywhere. Organic agriculture needs dung and manures. If you go for dairying for manure purpose it works out costly. Sheep and goat is the better option. These small ruminants are like debit cards for farmers. Goat is popular for milk as well. Surplus milk after feeding the kids is for the farmer. Hence it is called as poor mans cow. Fat globules of goat milk are small and hence it is easily digestible. It has some anti-fungal and anti-bacterial properties also. Goat milk is good for allergy and asthma patients. Goat can be milked at any time any number of time a day. Even then milk production from goat is not a commercial activity in India on large scale. We do not have separate indigenous breed for milk. All are dual breeds. Meat and leather are the commercial products of goat.
China is world number 1 in goat farming. India stands 2nd. According to the animal census of 2003 China has 195 million and India has 125 million goats. Population of goat is double to that of sheep in India. West Bengal has 19 million, Rajasthan 17 million and Uttar Pradesh has 13 million population of goats. Karnataka has 4.5 million goats, which is almost half of the sheep population. Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are popular for sheep. But now goat farming is getting momentum. Goats from these states are being sold in neighboring states.
Specialties of goat
Goat prefers to browse on leaves at height and likes herbage with more fibers. Grazing on the ground is hardly 10%. But it can be reared only with green grass in stall feeding system. Leaves need not be given. Goat needs double amount of fodder compared to sheep and fast growth. Goat meat is slightly fibrous and hard. But the fat content is less and hence it is good for health. Minimum 2 kids per kidding is the major advantage of goat. It gives even 3 to 4 kids sometimes. Hence the multiplication of goat is very fast. Milk production is sufficient even it has 2 to 3 kids. Goat has some peculiar naughty behavior. It is very sharp and active. More care is necessary on health management. Disease resistance is good, but the vaccination and regular de-worming is compulsory. Kid mortality is more if enough attention is not given. Forest area is decreasing every year, which has affected traditional goat farming. The forest department avoids browsing in the forest. But the scope for stall fed goat farming is excellent.
Traditional goat rearing
Traditional or grazing method of sheep and goat farming is in trouble due to shortage of labor and grazing land. Forest is fenced in many states to avoid browsing. Goats come back with half stomach filled in summer. It is difficult to get even drinking water. Pathogen and parasite infestation is more in grazing goats. Problem of worms is persistent in forest regions and areas with medium and heavy rainfall. Spreading of contagious diseases is more and fast in the grazing herd. Growth is slow and less even though the cost of rearing is less. Most of the traditional farmers keeping goat and sheep are landless and poor people. They do not provide fodder and feed at home. Grazing goats spend lot of energy on wandering for food. Traditional farmers depend on local breeds which cannot gain more weight. Though it is the livelihood for them, it rarely gets commercial importance. Hence stall feeding is the only solution for commercial and viable farming of goats. This article explains stall fed system of goat rearing.
Suitable climate for goats
Basically goat is comfortable in dry climate. But it tolerates low temperature. Humid condition is not suitable. However, goat farming is possible under stall feeding with platform system in heavy rainfall regions. Of course the goat can tolerate higher humidity than sheep. These small ruminants suffer with problems like cold, cough, HS, CCPP etc. in marshy places. Low temperature with less humidity is acceptable.
Stall fed goat farming
Housing for goats
By nature, it prefers to stay at height above the ground. But still it can be reared successfully on ground in dry regions. In heavy rainfall areas with high humidity platform system is inevitable. Slotted wooden platform is made at 5 feet height above the ground. In China fiber platform is in use. Urine and pellets dropdown and the goats remain clean. Collect the pellets every day or at least once in a week. In this method goat is free from ammonia smell of the urine. Goats remain healthy. Mud floor below is good. It absorbs the urine. If the height of the platform is 5 feet, cleaning is easy. Let the height of the shed be 8 to 10 feet in the middle and 5 to 6 feet on either side. This height is necessary to avoid heat during hot summer. Let the shed be in East-West direction in length to avoid direct sun inside the shed. Even the pellets on the ground keep moist. Roof may be of AC sheet, tiles or palm leaves. Each adult goat needs 10 square feet built-up space. Platform system accommodates more number of goats.
Open paddock of double size next to the shed is necessary. Trees around the farm keep the atmosphere cool. Put wire mesh fence covering the shed and paddock. Wooden steps are made for the entry and exit of goats. Steps are better for pregnant does. Let the door of the shed be kept open always so that the goats come out and go inside as and when they feel. If the bench like structure is made in the paddock, goats get on and sleep. Few farmers provide feed and water in the paddock itself. Shed is only for night stay. This is good for clean maintenance of the shed. Goats are kept in separate groups based on sex, age and body weight. Hence necessary partitions are made in the goat shed.
Generally, feed is given by keeping the goats inside the shed. Troughs are attached from outside all along the length of the shed. Feeding is easy and shed remains clean. If the trough is made with GI cleaning and maintenance is bit difficult. But it can be fabricated in any size and shape. Few farms have troughs made out of halved PVC pipes of 10-inch diameter. Maintenance is easy and durability is more. But the depth is less and hence the wastage of feed is more. It is better to go for 12 inch PVC pipe. Drinking water may also be given in these troughs itself. Clean the feeders before feeding once in a day.
Breeds of goat
Now let us study common breeds of goats reared in India. Beetle, Jamnapari, Shirohi, Malabari or Talacheri etc. are the popular breeds. Few farmers have world popular breeds like Boer and Damaskus. Deccani, Oosmanabadi etc. are the local breeds of Karnataka. Likewise, each state has its own breed. But most of the local breeds gain maximum of 30 kilograms in 2 years. Hence are not viable for commercial stall fed farming. Cross breed kids grow better and fast. Hence go for cross breeding.
Now let us go in detail about the goat breeds suitable for stall fed system. First one is Talacheri or Malbar, a popular breed of south India. Though it produces good amount of milk, it is a meat breed. Talacheri goats are seen in white, brown and black colour. Tip of the ear is in V or U shape. Doe gains 40 to 45 kilograms and the buck 60 to 70 kilograms. Buck can grow up to 100 kilograms. Dressed meat yield is 60%. Meat is smooth and expands while cooking. It is in attractive rose color. Disease resistance and adaptability of Talacheri breed is excellent. It gives minimum of 2 kids per kidding. Often it delivers 3 to 4 kids.
Second one is Shirohi. Body color and shape are very attractive. Shirohi doe yields more milk and the growth is also better. Average body weight is 70 to 80 kilograms. It can gain up to 100 to 120 kilograms. Taste of the meat is good. Only one kid per kidding in pure breed is the main drawback of Shirohi. But its cross breed gives 2 kids. Since milk yield is more doe takes 3 to 4 months to come in to oestrus after kidding. Hence maximum 3 kidding is possible in 2 years. Shirohi goat adapts very well to various climatic conditions.
Jamnapari is another popular breed from Uttar Pradesh. This grows to a size of a small cow. This being a milk breed yields 2 to 2 liters of milk per day. Doe needs 4 to 5 months to come in to oestrus after kidding. Roman nose, long ears and bunch of hair on the back are the characteristics of Jamnapari breed. Ears close the eyes while feeding on ground, which is called ear blindness. It cannot graze short grass because of Roman nose. But there is no problem in stall feeding system. Jamnapari goat gives one kid per kidding generally. 2 kids are very rare. This big goat gains up to 100 to 120-kilogram body weight. 90 to 100 kilogram is very common. Sometimes this big body size itself is a problem for marketing. Meat is fibrous and hard. And hence it is not preferred in some regions. Due to the body size and growth rate it needs more feed and fodder. Adaptability in various climatic conditions is also poor. Jamnapari is a fancy breed in many regions and is being used for cross breeding.
Boer is a world popular meat breed from South Africa. It is a dwarf goat with attractive body color and shape. It gains 100 to 120-kilogram body weight. Adaptability of pure breed goat is poor. Population of this breed is very limited in India and is being used for cross breeding. Pure breed Boyer buck costs about INR 30,000 to 35,000 now. Of course the Beetle goat from Punjab is also equally good. Hence the farmers need not run behind this Boer breed. Here we can conclude that Shirohi and Talacheri breeds are advisable for common farmers. Boer, Jamnapari and other costly breed bucks may be kept for the purpose of cross breeding. Talacheri-Shirohi does and Jamnapari-Boer bucks are the good combinations for cross breeding.
Breeding
Does and bucks mature by 8 to 10 months. But use them for breeding only after 12 months. Does and bucks selected for crossing should have body weight matching to their age. Good ancestry records and stable health are also important. There is no particular breeding season in stall fed goats. But avoid full pregnancy in hot summer. Excess temperature may cause abortion or pre-mature kidding. Doe comes in to oestrus again after 18 days of kidding in some breeds. But allow crossing in next heat. Artificial insemination is not popular in goats in India due to less rate of conception. Hence keep one good buck for 20 to 25 does. Keep 2 good bucks of different breeds in a herd of 30 to 35 does coming in to oestrus. Doe in heat will select the buck in which it is interested. In big farms bucks are shifted from group to group every week. Good does with regular kidding are retained for breeding for 5 to 6 years. But change the buck every year. Otherwise inbreeding creates retarded growth and many other health problems. Big farmers multiply pure breed goats and sell to new farmers. Common breeds like Shirohi, Talacheri etc. are sold for 250 rupees per kilogram body weight for breeding purpose. Special breeds like Jamnapari, Boer and Damascus etc. are costly and are charged animal wise.
Select big does of 40 to 45-kilogram body weight for cross breeding with Jamnapari and Boer bucks. Otherwise doe will face problem in kidding. Newly born kid of Shirohi and Talacheri breed weighs 2 to3 kilogram, Boer 4 kilogram and Jamnapari 5 kilograms. Gestation period is 145 to 150 days. Clean the slime in the mouth and nose immediately after the kid takes birth. This is to facilitate easy breathing. Collect the placenta and through it at a distance from the farm. Kid should suck colostrum within half an hour. This is most important for the development of disease resistance. Kid needs our assistance for feeding for 2 days. Goat produces enough milk even for 2 to 3 kids. 100 ml milk for 1-kilogram body weight per day is necessary. That is, if the kid weighs 3 kilograms it needs 300 ml of milk per day. Divide this amount in to 3 parts and feed in the morning, afternoon and by night. Feed the delivered doe with more fibrous feed. Stop giving oil cakes 1 week before kidding. Kid suffers with indigestion if the fat content in the milk is high and feeding is heavy. Kid may die due to yellow diarrhea. Doe produces surplus milk for 10 days. Take out excess milk by hand. Keep only necessary amount of milk in the udder and leave kids for feeding. Otherwise kids suck whole amount of milk. If the milk production is too less or the mother dies, feed the kid with goat or cow milk with the help of a bottle with a nipple. Keep the kids with their mother for 10 days. Later on keep them separate and leave them for feeding thrice a day. Otherwise the kids will not try to learn eating feed and fodder. Wean the kids after 1 months. Milk production continues even up to next kidding in Talacheri goats. Milk them regularly without fail. Otherwise it will lead to mastitis. Excess milk production itself is a problem in goats. Mortality of kids goes up with poor feeding management. Mother also gets in to trouble. It is better to keep small kids in guard rails for 2 weeks. Keep kids in sheds in the winter. Electric bulb may be lit to raise the temperature inside.
Both does and bucks develop horns. Long horns trouble the goats while feeding in the shed. This problem is more in bucks. Hence dehorn the kid within 10 days with hot iron rod or caustic potash. Let the trained veterinarian do this delicate job. Likewise hoof trimming is done immediately after the birth of the kid. Sometimes the hooves grow again which needs trimming. Otherwise it gives trouble in walking. Marking tag may be put to facilitate maintaining records. It is compulsory for insurance. Good bucks are in great demand. But castrate the other bucks which are not useful for breeding before 5-6 months. This helps for better growth and good quality meat production.
Feed management
Now let us study the feed management in goats. Silage is not yet popular in goat farms. Goats are fed with green fodder twice and concentrate once a day. It eats dry fodder like paddy straw. But it is not helpful for growth of the goat. However, the herbages of dicot plants like horse gram, cowpea, black gram, ground nut etc. are excellent. Improved green fodder varieties like CO-4, AP-01 and guinea are used in most of the farms. Yield and quality of AP-01 is better than other types. You may grow hedge lucerne in mixed cropping with the grasses. Few farmers use brush cutter for the cutting of the grasses. If the fodder crop is in the vicinity of the goat shed, 4 labors can maintain 400 goats. Fodder crop in 1-acre land is sufficient for 30 to 35 goats. Perennial tree fodders like Subabul, hedge lucerne, Gliricidia, mulberry etc. may also be fed. Nutritious green fodder reduces the dependence on concentrated feed. Cost of rearing of goat comes down. Locally available fruits can be given to goats. 1 kilogram of fodder and 100 grams of feed are necessary for 10 kilograms of body weight. For an adult goat 4 to 5 kilograms of green fodder and 400 to 500 grams of concentrate is sufficient. Feed may be divided and fed twice with the fodder or separately. 10 grams of mineral mixture per goat per day is compulsory with the feed.
Cost of readymade feed is very high. Nutrient content is also not assured. Hence feed may be prepared on the farm itself. According to animal nutrition experts feed composition must be like this- Broken maize- 40%, Wheat polish 30%, Dicot gram powder- 10%, broken rice 10% and soya been 10%. Add 1 kilogram of common salt, 2 kilograms of mineral mixture and 1 kilogram of digestible crude protein or DCP to 100 kilograms of main feed mixture. Pregnant and delivered does are given normal amount of feed only. It needs more feed if it has more than 3 kids. Generally small amount of oil cake is mixed in drinking water. Some farmers put common salt also. Goats like this and drink.
Silage making
Silage is the best food for goats. Now let us study the scientific method of silage making. Though the silage is useful, is not yet popular among goat farmers. Yellow maize is grown for silage making. Just after milky grain stage, that is by 85 days crop is harvested with cobs. Generally sunken silage pits are in use. Normally stone slabs are used for flooring and wall. It is helpful to control rats. Put thick plastic sheets on all side of the silo pit. Even the cement or stone pit needs plastic layer. This retains moisture in the silage and prevents air and water entering inside. Silage making is the anaerobic fermentation of fodder. Silage gets spoiled if air enters inside.
Cut the fodder with the cob to quarter inch size. Let it fall directly in to the pit. If the dicot plants are mixed the nutritive value of the silage will be better. Dissolve 20 kilograms of Jaggary (or molasses) in 150 liters of water in a barrel. Put 50 liters of water in another bowl and mix 250 grams of silage microorganism culture. Few private labs produce this silage culture mixture. This costs about INR 13,000 to 14,000 per kilogram and is sufficient for 100 tons of fodder. This is most important for good quality silage and also for easy digestion. Silage without culture may sometimes create diarrhea in goats. Mix this culture solution in to the Jaggary water. Sprinkle this solution at the rate of 10 liters per ton of fodder. 1 kilogram of common salt per ton of fodder is also added.
Complete the filling of the silo pit on the same day. Do not continue for the 2nd day. Trample the fodder in the pit by clean-bare feet so that the air inside the heap comes out. Cover the pit with plastic sheet to make it airtight. Put stone or sand bags on it. Silo-pit with 20 tons of fodder needs 5 tons of weight. Prevent the rain and flood water entering the silage pit. Rat should not burrow inside. This allows air and insects inside spoiling the silage. This fodder turns in to silage after 15 days of filling and keeps good up to 2 years. Size of cutting, amount of trampling and the weight on the top decides the quality of the silage. This silage is good even for sheep, cows and buffalos.
One cubic feet space of the pit holds 12 to 15 kilograms of silage. A pit of 30 feet length, 6 feet width and 10 feet depth (or 1800 cubic feet) accommodates 25 to 30 tons of silage. It is difficult to take out the silage if the depth of the pit is more than 10 feet. Do not open the entire silo pit while using the silage. It is better to open 2 to 3 feet of the length of the pit and exhaust up to the bottom. Silage can be prepared even with rain fed fodder sorghum varieties like SSV-73, PVK-01, GD-65195 and GD-65174. These also yield 10 tons of fodder per acre. Harvest and cut the fodder along with its grains irrespective of the variety. This contains 10 to 15 % of grain by weight. Hence the goat eating 2 kilograms of silage will get at least 200 grams of grain. One can escape from using concentrates if this kind of silage is fed. Silage culture used enables easy digestion and increases the availability of nutrients. Indigestion is not seen even if the goat eats excess quantity of silage. Yellow maize yields 15 tons of biomass per acre. 40 to 50 tons of fodder is available from 3 crops in a year. Each adult goat needs 1 to 1 tons of silage per year. So, one can raise 30 to 35 goats with 1 acre of fodder. Do not forget to use organic manure and micro nutrients to the soil for this continuous crop. Crop rotation is still better. 60 to 65 % is the optimum moisture content in the fodder to get good quality silage. If the silage contains more moisture goat suffers with the shortage of dry matter.
Yellow maize is excellent for silage production. But it will not come up well in high rainfall and low fertility areas. One can go for CO-4, AP-01, Guinea or any other improved fodder grass for silage making. Or it may be fed as green itself. In this case 2 kilograms of Jaggary (molasses) per ton of fodder is advised for good quality silage production. But this silage contains no grains. Hence feeding concentrates is inevitable. Using silage avoids the hectic work of fodder transportation and cutting every day. Thus reduces the labor requirement on regular days. Availability of nutrients is more in the silage than green fodder.
Management of goat farm
Goats drink less water. Even then 4 to 5 liters of water per goat per day is necessary in hot summer. Hence the water troughs are kept with feeders in the paddock. In some farms water tubs are kept inside the shed. Goats are given bath once in a week in summer and once in a month during winter. A mixture of lime powder and bleaching powder is spread on the platform and on the floor below once in a month. Then wash the platform thoroughly with water. Give white wash to the walls at least once in a year. Put 10 ml of 5% formalin in 1 liter of water and spray thoroughly to the shed on all sides. Send the goats out while spraying formalin. All these steps maintain hygienic condition in the shed and thereby keep the goats healthy.
Pellet is the best manure. It has 2.4 % Nitrogen, 0.88 % Phosphorus and 1.99 % Potash. One adult goat produces approximately 500 kilograms of pellets in a year. Collect the waste fodder and pellets regularly and heap them at a distance. This manure may be used for fodder or other crops. It has good demand and price.
There is one simple method to assess the age of goat. Like other animals, kid will have milk teeth. Two permanent teeth appear by 12 to 14 months. By 18 to 20 months goat will have another pair of permanent teeth. Goat gets 6 permanent teeth by 26 to 28 months. Last pair of permanent teeth will emerge by 36 months or 3 years, which indicates the completion of growth. By 7 to 8 years teeth start depreciating.
Health management and Vaccination
Goats do not have wool cover like sheep. Here the infestation of ecto-parasites like lice ticks etc. is more. Goat may be dipped in water tank with suitable chemical. Spraying of the insecticide or injection is also in practice. De-worming is most important for the control of endo-parasites. Worm infested goats suffer with debility and lose weight. Put first doze of de-worming medicine at 4 to 7day stage for newly born kids. Later on de-worm once in a month for 1 year. De-worm the adult goats once in 3 months. De-worm the pregnant doe after 2 months of conception. De-worming earlier to this may lead to abortion. Mark the goats with dye after putting the medicine. This is to avoid double doze or missing. Use different medicines each time. De-worming injections and combined medicines for many endo-parasites are available now. There are many chemicals and brands. The dosage depends on the body weight of the animal. Hence it is better to depend on an expert veterinarian for any medication. Test the pellets in the lab once in 6 months for endo-parasites. De-worming is most important for good health and growth of goats.
Most of the diseases of sheep are seen in goats also. PPR, ET, Goat Pox, FMD, HS, Anthrax etc. are common. Vaccines are available for all these diseases. Prepare a schedule of vaccination and follow it without fail. Hence the stall fed goats escape most of these diseases. Treat incidental health problems like cold, cough, fever, wound etc. as and when required.
PPR and ET vaccines are compulsory twice a year for stall fed goats. Put first doze of PPR vaccine by 2 to 2 months to the kid. Booster dose after 17 to 21 days is also necessary. Give 1st dose of ET vaccine at 2-month stage. Booster dose after 17 to 21 days may also be given. Put HS vaccine to the kid at 3-month stage. Give 1 dose of PPR vaccine and 2 doses of ET and HS vaccines per year for adult goats. Foot and mouth disease or FMD is more common in goats than sheep. Put FMD vaccine twice a year in outbreak areas. Goat Pox is also a dangerous disease. This vaccine once in a year is necessary in infested areas. Makreshwara Goat Research Station of Uttar Pradesh has developed a trial vaccine for goat pox and is found effective. Avoid entry of diseases while bringing goats from other farms and regions. The possibility and intensity of these diseases vary from region to region. Hence it is better to consult an expert veterinarian of the locality while planning vaccination schedule. Mastitis is another major problem of goats. Take out surplus milk and avoid the possibility of mastitis. Regular vaccination avoids all these diseases in stall fed goats.
vaccination for goats
Economics of goat farming
Goat is a fast growing animal. It gains 4 kilograms per month in stall feeding with nutritious food and good management. This speed of growth is up to 6 to 8-month age. The meat quality is excellent at 7 to 8-month stage or at 20 to 25-kilogram body weight. Hence it gets premium price and demand. Aged goat yields fibrous hard meat. Dressed meat percentage is less in goats used for breeding. Hence 8-month age is the right stage for culling. Live goat gets half price of the dressed meat. That means if the meat price is rupees 300 per kilogram, live goat gets 150 to 175 rupees per kilogram body weight. Breed, age, body condition and customers choice etc. decide the price of the goats.
Traditional goat farming is very common in India. But the systematic and commercial stall feeding system is very rare. Marketability of the goat meat is excellent. Rearing sheep and goat in combination is also good. Though goat needs more food and attention its fast multiplication generates more income. We can achieve better with systematic stall feeding in goat farming. This is the right time to reap the best opportunity for goat rearing. Let us hope our farmers will come forward and bring India in to number one position in goat farming in coming years.
Steps that need to be taken before starting a goat farm.
- Selection of land where you are willing to start a goat farm
Selection of land to start goat farming is the very first step you are going to take. There is no any hard and fast rule to stick with the land selection whatever the land you have is good to go or it would be better if you have surplus land at the city out skirt with the greenery and grazing area.
In my case I have only 32 decimile of land with enormous grazing field out of which i am using 21 decimile for shed and fenced area and remaining for the servant quarters as you must provide the rooms for the care-taker who are going to stay there 24×7.
Do the proper fencing of the land with the boundary wall or bamboo fencing but i would suggest for the brick and cemented boundary provide more security to the place or it could be your choice mainly it depends on the surrounding and the security concern of the farm.now you have a good fence i.e the boundary wall with the proper entrance. Now it is the time for goat shed construction.
- Goat shed construction plan
A proper cleaned, hygienic and spacious shed is required for the better growth of your goats. Depending upon your land area,expenditure and farm strength the shed area may vary. As in my case i have a shed for 100 goats for which i have used 60×18 feet(i.e 60 feet of length and 18 feet is width. )
The dimension of the shed depends on your choice whether it could be less or more as i mentioned but i would suggest to give a try with the smaller strength i.e shed for 100 goats.
In general it is being suggested that for one goat there must be 10sq ft. Area is needed but this can be less or more mainly it depends on the breed and age of goat whether it is adult or kid.
I assume you have selected your dimension of the shed now its time to build the shed. Use bricks and cement for the shed wall. 12 feet of height must be maintain and a proper ventilation is needed. For the roof area use better quality of asbestos which is good heat absorbent in summer.
Create one water reservoir or cemented tank to provide fresh drinking water supply to goats every time. it should be outside of the shed area. Build a bamboo fence out side the shed for proper movement of the goats.
Proper cemented or steel stall is required for the goat feeding it must be inside or outside the shed.
So as to summarize:
Shed construction plan for 100 goats:
- Shed dimension in my case it is 60×18 feet.
- Wall height is 12 feet.
- Bamboo fence outside the shed.
- Material used for shed is brick,cement and asbestos.
- Cemented tank for the fresh drinking water for goats (Outside the shed inside the bamboo fence)
- Bore well equipped with motor or submersible pump for the fresh drinking water for the goats.
- Feeder stall may be cemented or steel menzer for feeding. Have long cemented feeding stall inside the shed and steel menzer or feeder for outside feeding.
- Selection of Goats Breed
Goats breed selection is very important aspect in the goat farm as this is the main asset of your business which is going to give your business a boom and a good uplift. Selection of breed is very important point in profitable goat farming business plan.
There are different breeds out there which is considered as profitable breed selection basically it depends on the region and climate there are many breeds available but i am covering some of them which is considered profitable for north india region. They are categorized in two part.
Pure Breed Selection.
- Sirohi
- Jamnapari
- Tota Pari
- Barbari
- Beetel
- Black Bengal
Cross Breed Selection.
- Cross breed of sirohi and black bengal (sirohi buck and black bengal doe)
- Cross breed of jamnapari and sirohi (jamnapari buck and sirohi doe)
- Cross breed of black bengal and beetel. (beetel buck and black bengal doe)
There may be a number of cross breed selection depends upon the breed of Buck and Doe.The rule of thumb in breed selection is the environmental and climatic condition where the breed is best suited for. For example:
- Learn cross breed concept in goats
Sirohi the goat breed of sirohi district of rajasthan is well suited with the Rajasthan hot and dry climatic condition. If you want to raise pure sirohi breed in different region of india apart from the rajasthan the mortality rate increases because of the climatic condition with which they are not adapted to.
But what if we want Sirohi breed in our farm. As in my case i have Sirohi breed too, here comes the Cross Breed Concept.
All you need a cross breed Sirohi i.e take a female mother goat(doe) of your area. For example in Jharkhand climates are very hot in summer and chilled in winter the Black Bengal breed is well adapted with Jharkhand climate.
So take black bengal doe and sirohi Buck the first cross of the product would be 70% sirohi or 30% black bengal (Note:the percentage genetical behaviour may vary depends on the mating breed.) Now this breed would be well adapted with the jharkhand climate.same apply with the other breeds too.
- Learn about vaccination schedule
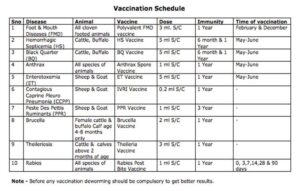
Proper Scheduled Vaccination is very important to overcome the mortality rate in goats. Here i will be covering every vaccine shedule which is i am following in my farm.
After goat purchase and before entering into the goat farm deworming is compulsary and following vaccine must be scheduled.
The Common vaccine schedule prescribed by doctors are:
- FMD(Foot and Mouth disease) vaccine name is polyvalent FMD vaccine given once in a year dosage is 3ml. S/C given in february & December.
- Anthrax vaccine name is anthrax spore vaccine given once in a year dosage is 1 ml.S/C in the month of May -june
- ET(Enterotoxemia) vaccine name is ET Vaccine once in a year dosage is 5 ml.S/C in the month of May – june
- CCPP(Contagious Caprine Pleuro Pneumonia) or IVRI Vaccine dosage is 0.2 ml S/C once in a year.
- PPR(Peste Des Pettis Ruminants) or PPR Vaccine with a dosage of 1ml S/C given once in a 3 Year.
- Fodder planning for Goats
Goat fodder plan is very important aspect of the goat farming a proper fodder plan and cost management of fodder is required to make good profit in this goat farming business. Here in this section i will discuss how to make an effective fodder to boost your goats growth in lesser time also i will discuss the different feeding style like complete stall fed system and partial stall fed system.
In addition with the dry fodder green fodder is very important to provide essential nutrients to the goats. Grazing of goats is very important for this you must have a surplus grazing area with greenery so as for proper movement of the goats which helps in their digestion and enhance metabolism.
Generally in my goat farm i prefer partial stall fed system that is goats are given dry fodder or booster in the stall fed condition and freed for grazing from morning 11 to 3 noon. Then they enter the farm and again stall fed.
How to make goat dry fodder ?
The composition and Preparation Technique. To make fodder of 100 kg following are the ratio of composition (Note: I am using local regional language to describe the ingredients so as to benefit the regional readers.)
- Chokar – 45 kg
- Makai Darra – 25 kg
- Badam Khalli – 15 kg
- Korai (Chana chilka) – 12 kg
- Mineral Mixture – 2 kg
- Salt – 1 kg
These are the ratio which i am using and getting the positive result also the growth of the goats in farm is very high in almost 8 month kids become adult and acquire the maximum weight. This is the 100 kg ratio and may be used in any amount of fodder preparation.
This fodder must be mixed with kutti in half ratio and given. For example if kutti is 1 kg then mix this ½ kg fodder. Under the partial stall fed condition hence the almost all nutrients supplied by grazing this concentrate with kutti given twice a day i.e morning and evening 1 ½ kg twice for one goat means 3 kg every day (2 kg kutti and 1 kg concentrate).
Apart from this concentrate green fodder is also very important provide the goats with green fodder every day or leave them for grazing. There are many things to discuss and need to be cover hence i will write every topic in different post this was the only general idea you must stick with to start a goat farm.
- Minimise risk factors
You have to plan everything properly and one important factor for profit in goat farming is to minimise the risks involved in this business.
Compiled & Shared by- Team, LITD (Livestock Institute of Training & Development)
Image-Courtesy-Google
Reference-On Request.


