A.P. Urkude*, P.D. Vihol, J.H. Patel1, J.M. Patel
Department of Veterinary Pathology,
1-Department Of Veterinary Pharmacology,
College of Veterinary Science and Animal Husbandry, Navsari, Gujarat-396450*at.atul.94@gmail.com
ABSTRACT
Climatic change, higher temperature and extreme heat are emerging issues for human, livestock, pets and birds. Heat stress, also known as heat stroke, occurs almost in every summer and animals are more susceptible to it than humans. When animal’s body cannot cool itself enough to maintain normal internal body temperature, animal suffers from the heat stress, which leads to the health-related problems causing directly or indirectly loss in production and performance of animals. In heat stress condition, animal should be managed as soon as possible. Some additional managemental practices are need to be taken care in terms of strategies are need to be undertaken regarding shelter facility, ventilation system, water supply and feeding of animals to prevent occurrence of heat stress in sunny days of summer.
INTRODUCTION
Sunny days are here again…..!!!!
Summer season brings the longer and warmer days with fun of vacation and outdoor activities. But with changing environmental conditions, summers are getting hotter and hotter. Climatic change, higher temperature and extreme heat are emerging issues for human, livestock, pets and birds also.
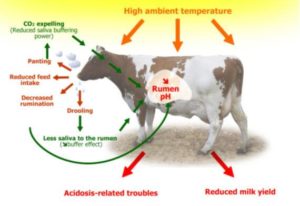
Heat stress also known as heat stroke is one of those conditions that occur almost in every summer. Animals are more susceptible to heat stress than humans. Its impact on livestock varies from animal to animal based on genetic makeup, health status, stage of production and previous exposure to heat. These factors along with the extreme environmental conditions (like high temperature, humidity, wind speed and cloud cover etc.) results in fatal condition in animals.
WHAT IS HEAT STRESS/HEAT-STROKE?
Heat stroke, is a form of non-fever hyperthermia that occurs when heat-dissipating mechanisms of the body cannot accommodate excessive external heat which causes an increase in body temperature and evokes a physiological response.
Heat stress occurs when an animal’s body cannot cool itself enough to maintain a healthy internal temperature. Cows feel hot 10-15°C sooner than we do.
It leads to deteriorated living conditions, reduced quality of life, and, in extreme cases, death of affected animals.
WHAT ARE THE EFFECTS OF HEAT STRESS?
A rise in the body temperature results in heat illnesses. Which directly or indirectly causes loss in production and performance of animal. Following are some of the heat stress effect in affected animals-
Reduced feed intake
Reduced weight gain
Poor breeding efficiency
Lower milk production
Decreased immunity
Increased disease susceptibility.
Changes in behavior
Death can result consequently.
HOW TO IDENTIFY THE SUFFERED ANIMAL?
It is quite easy to identify the affected animal by pointing out following signs in animal-
Animals seek shade and/or wind
Prefers standing than lying down
Increased production of saliva
Open-mouth breathing
Foam around the mouth
Water intake enhanced while feed intake reduced
Increased respiration rate, body temperature
Vomiting or diarrhea
Weakness, dullness
Collapse or seizure- uncontrolled movement and loss of consciousness.
*If the animal is showing above signs of heat stroke, move the animal immediatelyfrom area of direct sunlight to the cool shaded area and give ample amount of cool water to the animal.Increase air movement around the animal by using fans or ventilation. Contact nearby local veterinary doctor for further assistance.
MANAGING ANIMALS DURING SUMMER
Managing animals in boiling days of summer requires good forward planning. It requires to keep an eye on the weather forecast, and developing the plans for extreme days.
Extreme weather conditions can be managed by applying following measures-
1. Shelter facility
Animals need to be provided with good shelter facility during extreme days. Specifically, for very young or weak animals which are more prone to heat stress condition.
Treesaround the animal house provide cool shade. Temperature in the animal house can be lowered by spraying cool water on roof of animal house or by constructing sprinklers on roof.
2. Ventilation system
Animal shelter should be high enough off the ground to allow adequate movement of air.
It should be provided with windows and exhaust system.
Fans in the animal shelter improves the ventilation system by fresh air exchange.
3. Water supply
Water is essential for maintaining internal body temperature within limits.
Provide ad libitum supply of clean and cool drinking water to the animals.
Water troughs and containers should be large enough to have easy access and should be kept clean.
4. Wetting of animals
It is one of the good ways to deal with high temperature conditions.
This can be done by manually spraying water on animals or by using sprinklers constructed inside the shelter.
5. Handling of animals
It is recommended not to handle animals in extreme conditions. Transportation of animal in sunny days may expose animals to heat stroke.
Animals for draught purpose should be use as early or late in the day as possible when temperatures are lower.
Animals should be given rest during noon hours.
Stocking density of animals should be reduced.
6. Feeding management
Decrease in appetite is seen in animals during hot weather.
Ration should be formulated so that the heat production in animal should be minimize.
High fiber diet, good quality forage, grains and fats should be used in feed.
Mineral content (especially potassium, sodium, magnesium) of feed should be increased.
Anti-stress supplement can be used in feed and water.
CONCLUSION
With the changing environmental conditions, animals are becoming more prone to heat stress in sunny days. That leads to the issues related health and production of animals. So, to reduce the risk of heat stress in domestic animals, special care related to their health, shelter facility, feed and water need to be taken care.


