Concept of Reproduction in the Canine and Feline: PRACTICAL TIPS
Nutshell of Reproduction in the Canine and Feline
DR. RAKESH SINGH,TVO, MOTIHARI
The Canine
Bitch
- Puberty – 6 mo.
- Monoestrus
- One estrus during breeding season
- Estrous Cycle
- Proestrus
- Estrus
- Metestrus or Diestrus
- Anestrus
Estrous Cylce (Non-Pregnant)
- Proestrus (9 days)
- Vulva swollen
- Bloody discharge
- Attracted to male but does not mate
- Estrus (9 days, ovulation day 2)
- Accepts male
- Straw-colored discharge
- Metestrus or Diestrus (90 days)
- False pregnancy
- Anestrus (5 months)
- Sexual inactivity
Estrous Cycle – Pregnant
- Proestrus (9 days)
- Vulva swollen
- Bloody discharge
- Attracted to male but does not mate
- Estrus (9 days, ovulation day 2)
- Accepts male
- Straw-colored discharge
- Pregnant Metestrus/Diestrus (50 – 60 days)
- Pregnancy
- Parturition (63 days from ovulation)
- Anestrus (5 months)
- Sexual inactivity
- Occurs during estrus
- Length of courtship by male is variable
- Licks vulva
- Bitch stands with tail to one side
- Mounting
- Male mounts without erection and penetrates
- Os penis
- In vagina, male bulbus glandis engorges, thrusting
- Male dismounts and turns around but penis remains in vagina “the tie”
- Ejaculation
- Tie last 5 min to 1 hour
Canine Mating

- Mate 2 times
- Days 11 and 13 after start of proestrus
- Sperm lasts up to 7 days in female
- Infertility
- Often from mating not at appropriate time
- Hormonal detection of ovulation
- LH increase associated with progesterone >0.5 ng/ml
- Ovulation progesterone 2-5 ng/ml

- Days 11 and 13 after start of proestrus
Pregnancy
- 63 days (58-68)
- Range due to dating from breeding not fertilization
- Hormonal Changes
- Similar to not mated
- Progesterone maintained higher
- CL required to maintain pregnancy
- No placental progesterone
- Placental relaxin
- Drop in progesterone triggers parturition
- Detection
- Adominal palpation at 3 – 4 weeks
- Ultrasound after day 16
- Parturition
- Hormones similar to other farm animals
Parturition
- Delayed Parturtion
- Primary inertia
- Does not show signs of parturition
- Does not progress from stage 1 – stage 2
- If green fluid, Caesarian
- Give oxytocin in several small doses
- Secondary inertia
- Uterine exhaustion
- Oxytocin
- Primary inertia
Estrus Control
- Induction
- eCG
- Prevention
- progestins
Disorders of the Bitch
- Cystic endometrial hyperpalsia (pyometra)
- Uterus fills with fluid
- Progesterone increases first
- Contamination of uterus by vaginal bacteria
- Toxemia results from absorption of fluid and endotoxins
- Thirst,vomiting, inappetence, shock, death
- 4-6 weeks after estrus
- Bitches >9 years that have not had a previous pregnancy
- Can be open or closed
- hysterectomy
- Uterus fills with fluid
Pyometria in a 10 year old bitch
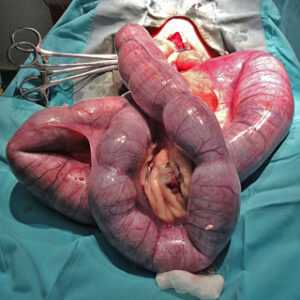
Disorders of the Bitch
- False pregnancy
- Normal to some extent
- 60 days after estrus
- May lactate, gain weight, nesting behavior
- Mammary tummors
- Thought may be related to similarity to pregnancy and non-pregnancy
Disorders of the Male Dog
- Hypersexuality
- Castrate
- Progesterone
- Cryptorchidism
- Normal descent at days 7-10 after birth
- Should be removed if retained for >1 yr.
Artificial Insemination
- Bitch does not accept the male
- Shipment of semen
- Minimize the number of breedings
| Semen Collection in Dog | ||
|
|
||
Insemination of the Bitch
- Bitches ovulate around day 10 after they enter proestrus (discharge) or about 1 – 2 days of estrus.
- Ovulation can be detected by:
- LH assay (peak LH value + one day)
- Progesterone assay (>5 ng/ml)
- Cytology of vaginal smear (>50% cornified cells)
- Ovulation can be detected by:
- Remember oocytes in the canine are ovulated as 1° oocytes and must mature in the oviduct to a 2° oocyte before fertilization.
- Fresh or cooled semen, inseminate 2 days after ovulation detected and again 48 – 72 hr latter.
- Frozen semen, inseminate on day 5 – 7 after ovulation
- Uterine insemination better than cervical
Feline Reproduction
- Domestication?
- Female-Queen
- Male – Tom
- Puberty
- 6 – 9 months
- Estrous Cycle
- Seasonal
- January to September
- House cats may cycle year round
- Seasonal
Estrous Cycle
- Pro-estrus
- 1 – 2 days
- Attracted to males
- Rubs head and neck on objects
- Vocalization, posturing and rolling
- Estrus
- Accepts male
- 4 – 6 days if male present, 10 days if no male
- Ovulation 27 hours after mating (induced)
- Affectionate to aggressive towards owners
Estrous Cycle
- Proestrus if queen did not ovulate
- 8 – 10 days
- Diestrus after ovulation
- psuedopregnancy – 40 days
- pregnancy – 60 days
- Anestrus 3 – 4 months
Hormonal Changes
- Proestrus
- Estrogen increases due to follicular development
- Estrus
- Estrogen high until ovulation
- Ovulation 27 hr after mating (vaginal stimulation)
- Diestrus
- No Cl if mating does not occur, so no diestrus
- Cl produces progesterone (63 days, peak day 20)
- If pregnancy does not occur or fails, CL life only 1/2 that seen in pregnancy.
Mating

- Queens call or vocalize (low moaning sound)
- Owners may think a sign of illness
- During mating
- Tom bites neck female
- With erection penis faces forward
Mating
- Queens call or vocalize (low moaning sound)
- Owners may think a sign of illness
- During mating
- Tom bites neck female
- With erection penis faces forward
- Only lasts 30 seconds to 5 minutes
- As male dismounts female gives a loud copulatory call and Tom retreats
- Mating occurs 6 – 7 times until queen declines
- May occur for up to 4 days
Pregnancy
- 63 days
- Diagnonsis
- Adominal palpation day 17 -25
Parturition
- Similar to other species in events and hormonal control
- Dystocia rare – caesarian
- Uterine inertia – oxytocin
Control of Estrus
- Ovariohysterectomy
- Induction of Ovulation
- HCG
- Vaginal Stimulation
- Prevention of estrus
- progestins
Disorders of the Queen
- Psuedo-pregnancy
- Mating to sterile male
- Vaginal stimulation or hormonal stimulation
- Cystic endometrial hyperplasia (Pyometra)
- Same as in bitch
- Failure to cycle
- Stress, poor nutrition, disease, inadequate light, cystic follicles
Diseases of the Tom Cat
- Spraying
- Castration
- Cryptochid
- Descended at birth
- Treatment is castration
- Reference-on request



